Blinkentree
(→Get the compiler toolchain) |
(→Get the compiler toolchain) |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
Then download the [[AVR Studio || http://www.atmel.com/forms/software_download.asp?family_id=607&fn=dl_AvrStudio4Setup.exe]] | Then download the [[AVR Studio || http://www.atmel.com/forms/software_download.asp?family_id=607&fn=dl_AvrStudio4Setup.exe]] | ||
--> | --> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Coding === | === Coding === | ||
Revision as of 18:42, 17 February 2011
| | |
|---|---|
| We built our own blinking X-mas tree for the market in Strassen. | |

| |
| Meetings: | none |
| Type: | hardware |
| Tracker: | https://source.hacker.lu/projects/blinkentree |
| Status: | concluded |
| Members: | |
| Contact Person: | slopjong (mail), prometheus (mail) |
| Tools | |
| QrCode: | 
|
Diese Seite gibt es hier auch in deutsch.
Contents |
Introduction
What is this flashing green fir tree about?
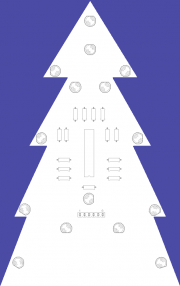
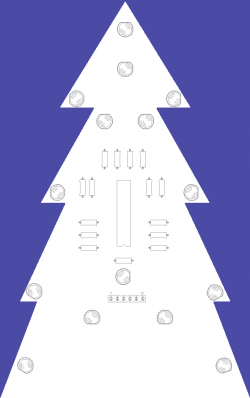
As creative hackers, we thought it would be necessary to support the Christmas market of the commune of Strassen with something tiny, but creative. Result? The Blinkentree. Obviously it represents a green fir tree that is dorned with flashing LEDs which should represent the baubles of a 'real' tree.
A big thanks to all of you folks who purchsed a Blinkentree and thus supporting syn2cat Hackerspace.
Hacky Christmas!
Assembling the kit
If you didn't buy a kit but an already assembled Blinkentree you can continue with the next section.
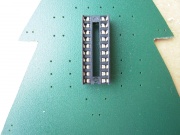
Otherwise follow the next instructions to assemble your kit. We recommend to first solder the resistors, then the chip socket and then the LEDs because it's easier to start with the small devices and finally solder the biggest ones.
- The resisostors have all the same value and they don't have any polarity so it doesn't matter what direction they're put on the board.
- The chip socket has an indentation which must be oriented down.
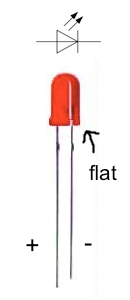
- The LEDs have a polarity. The long leg is positive (+) and the small one is negative (-). The current flows from the positive to the negative so you have to pay attention while you assemble the kit. The LEDs are flat on the negative side. You have to orientate the LEDs as shown on the second picture (click on it to resize it).
How to program it on your own?
The goal of our Blinkentree project was to offer you a christmas tree that you can reprogram. The flashing patterns can be changed by yourself. If you never have programmed before you might think that it's getting too complex now.
This is true if you don't want to learn something new. It's not true if you want to get new skills. This howto is intended to be understood by everyone. Even by those who don't know much about programming. If you come across stuff that's too unclear for you let us know and we help you (electronics[at]hackerspace.lu).
If you're completely new to the microcontroller world there are essentially four steps to be followed.
- Get the compiler tools
- Write the program
- Compile the program
- Get the compiled program into the microcontroller
Get the compiler toolchain
Before we start writing the program we must install the compiler. A compiler is a program which reads your program text (source code) and turns it into machine code which is a series of instructions that the controller will execute later. One instruction could be "set pin 3 of port B to high". Thus you could switch on an LED.
A very common compiler is the GCC compiler which is part of the WinAVR (Windows) and CrossPack-AVR (Mac). You might already have guessed it, we are using the C language here.
Windows users download WinAVR and mac users should download CrossPack AVR instead.
If you downloaded the windows version the installer will ask you to make an entry in the PATH variable. Be sure that the checkbox in the dialog is checked.
If you downloaded the mac version the installer will put the stuff into /usr/local/CrossPack-AVR [1]. Now the compiler should be on the PATH. You can check this by opening a terminal (shell) and typing inecho $PATH
There should be /usr/local/CrossPack-AVR/bin present. If not execute this to add it:
echo -e " \n \n export PATH=/usr/local/CrossPack-AVR/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.profile
Coding
Programming new flashing patterns for your Blinkentree is very easy. Here is a sample code:
#include <avr/io.h>#include <util/delay.h>int main(void) {
// configure the ports as outputsDDRD = 0b11111111;
DDRB = 0b11111111;
while(1)
{PORTB = 255;
PORTD = 0;
_delay_ms(400);
PORTB = 0;
PORTD = 255;
_delay_ms(400);
}}
Save this code in the file main.c because this filename will be used in next sections.
In the first two lines you include one library for input/output (I/O) operations and one library for delay operations. In line 4 you define the main function that the Blinkentree jumps to when you switch it on. The DDRD and DDRB functions are used to configure the ports D and B. They're set to 0b11111111 which are binary numbers where each 1 stands for one pin of the port which has 8 pins. 1 means that the pin is set as an output wheras a 0 would be used to configure the pin as an input.
By setting the port B to high (255 = 0b11111111) in line 12 we turn on all the LEDs of that port. If you want to turn on only certain LEDs you have to set other values from the range 0 to 255 (0b00000000 to 0b11111111). You can use the decimal-binary converter to convert decimal numbers in binary numbers.
The while loop is used to execute the flashing pattern repeatedly. Otherwise the microcontroller would stop at the end of the main function. In other words the flashing pattern would be executed only one time.
On Suhas's blog you find more information about the I/O operations. If we have some time we will update this site to provide you with a mini coding tutorial for AVR microcontrollers.
Compiling and linking
After you're done with the programming, the code must be translated into machine code that can be executed by the microcontroller. Open your command line and change into the directory where your code file is.
There you you type in:
avr-gcc -Wall -Os -std=c99 -DF_CPU=1000000 -mmcu=attiny2313 -c main.c -o main.o avr-gcc -Wall -Os -std=c99 -DF_CPU=1000000 -mmcu=attiny2313 -o main.elf main.o avr-objcopy -O ihex -R .eeprom main.elf main.hex
These commands are the same for Mac and Windows.
After that you have main.hex which is the translated code that will be loaded into the chip later.
Flashing the microcontroller
To flash the controller you need a programmer like the USBasp. On that homepage you find all information you need to build your own programmer but I'd recommend to come to our hackerspace in Strassen where you get help and support. We have the equipment like an etching machine to make electronic stuff in a professional way. If you have questions about our space just write an email to electronics[at]hackerspace.lu (please replace [at] by @).
Windows requires a driver for the USBasp but not Linux and Mac OS. There you can work with it immediately.
TODO: Driver installation for f***ing Windoze.
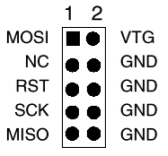
With the programmer you are now able to flash your controller. To connect the programmer with your Blinkentree you need to add a pin header on your board.The pins from left to right are:
1. MOSI | 2. MISO | 3. SCK | 4. GND | 5. VTG | 6. RST
On the USBasp you have this connector:
Connect all the pins with the same name. If you also connect VTG you have to switch off the Blinkentree and if you don't connect it you have to switch it on.
Then on your Windows machine you execute
avrdude -c USBasp -p t2313 -U flash:w:main.hex -v -F
and on a mac
sudo avrdude -c USBasp -p t2313 -U flash:w:main.hex -v -F
Note
If you replaced the chip by a new one you have to configure it first before you can flash with the last command.
Then you have to execute
avrdude -cUSBasp -p t2313 -U lfuse:w:0x64:m -U hfuse:w:0xdf:m -U efuse:w:0xff:m
on Windoze
and
sudo avrdude -cUSBasp -p t2313 -U lfuse:w:0x64:m -U hfuse:w:0xdf:m -U efuse:w:0xff:m
on a Mac.
References
Footnotes
- ↑ /usr/local/CrossPack-AVR is just a symbolic link to /usr/local/CrossPack-AVR-20100115 or something like that.